Chapter 7 Revenue
Meaning: It is the money payment received from the sale of a commodity.
Total Revenue: It refers to the total money realised by selling the total output.
TR=P * Q
TR = ∑ MR
TR=AR * Q
("*" this is the symbol of multiplication)
- Average Revenue: It is the per unit revenue generated by selling an unit of an output.
- Average revenue and price are the same
we know AR is equal to per unit sale receipts and price is always per unit. since sellers receive revenue accordingly to price, price and AR are one and the same thing.
This can be explained under as:
TR = quantity * price
AR = TR
quantity
= price * quantity
quantity
AR= price
AR curve and the demand curve are same.
("*" this is the symbol of multiplication)
- Marginal Revenue: It is an additional revenue generated by selling an additional unit of an output.
MR = change in TR
change in N
OR
MRn = TRn - TRn-1
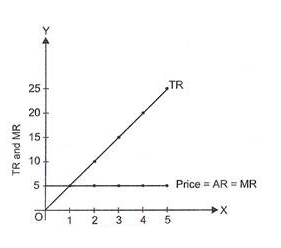
- Perfect competition:Because the product being sold is homogeneous it would be sold at uniform prices determined by the industry. Therefore AR & MR curves become Parallel to X-axis and TR increases at a constant rate.
schedule:
 Diagram:
Diagram:
- Imperfect competition: Here as the product are differentiated and close competition is here, so under both monopoly and monopolistic competition the producer would lower down the price to sell more output.
Schedule:

Diagram:
- Relationship between AR and MR
(1). When AR rises, MR also rises but MR > AR
(2). When AR is maximum, MR cuts its from above.(AR=MR)
(3). when AR falls MR also falls but MR falls at a higher rate.
- Relationship between TR and MR

(1). When TR rises at diminishing rate, MR falls but positive.
(2).When TR is maximum, MR is zero.
(3). When TR falls, MR is negative.
- Why MR < AR for a monopoly firm?
For a monopoly firm, MR < AR. This is because a monopolist can sell more only by lowering down the price of the product. In case AR is falling MR must be falling faster than AR.
Because a given fall in R is averaged out in estimation of AR.
- Break-even point: It refers to a situation/ output where the total revenue generated by the producers is equal to the total cost incurred by him.
At BEP a producer generates normal profit but no abnormal profits.
TR = TC
- Normal profits: It is the minimum return that the producer excepts from his capital invested in the business. These profits are a part of TC.
- Abnormal profits: These are the profits generated by producer over and above normal profits to join the industry.
Abnormal Profits = TR - TC
- Shut down point: It refers to the point or situation where the firm is just able to recover variable cost and not fixed cost.
TR = TVC
OR
TR/Q = TVC/Q
Here the firm is incurring loss of fixed cost.
- Most Important questions
Q1. why the average revenue is equal to the price?
Q2 .Explain the relationship between AR and MR.
Q3. Explain the relationship between TR and MR.
Total Revenue: It refers to the total money realised by selling the total output.
TR=P * Q
TR = ∑ MR
TR=AR * Q
("*" this is the symbol of multiplication)
we know AR is equal to per unit sale receipts and price is always per unit. since sellers receive revenue accordingly to price, price and AR are one and the same thing.
This can be explained under as:
TR = quantity * price
AR = TR
quantity
= price * quantity
quantity
AR= price
AR curve and the demand curve are same.
("*" this is the symbol of multiplication)
MR = change in TR
change in N
OR
MRn = TRn - TRn-1
schedule:
 Diagram:
Diagram:Schedule:

Diagram:
(1). When AR rises, MR also rises but MR > AR
(2). When AR is maximum, MR cuts its from above.(AR=MR)
(3). when AR falls MR also falls but MR falls at a higher rate.

(1). When TR rises at diminishing rate, MR falls but positive.
(2).When TR is maximum, MR is zero.
(3). When TR falls, MR is negative.
For a monopoly firm, MR < AR. This is because a monopolist can sell more only by lowering down the price of the product. In case AR is falling MR must be falling faster than AR.
Because a given fall in R is averaged out in estimation of AR.
At BEP a producer generates normal profit but no abnormal profits.
TR = TC
Abnormal Profits = TR - TC
TR = TVC
OR
TR/Q = TVC/Q
Here the firm is incurring loss of fixed cost.
Q1. why the average revenue is equal to the price?
Q2 .Explain the relationship between AR and MR.
Q3. Explain the relationship between TR and MR.


Comments
Post a Comment