CBSE Class 11 MICROECONOMICS Notes
Chapter 1 introduction
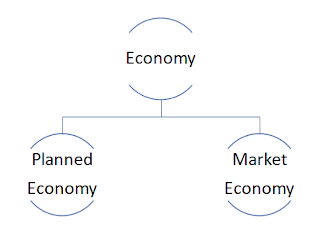
Economy: An economy is a system that provides people with the means to work and earn their living in the process of production.
1. Planned Economy : Economy in which everything is planned and determined by the central planning authority.
2. Market Economy : Economy in which everything is determine by the market forces of demand and supply.
you may also watch video of this chapter
Economics : It is the study of human behavior in the presence of scarcity.
(SCARCITY : scarcity refers to the limitations of supply in relation to demand for a commodity)
you may also watch video of this chapter
Economics : It is the study of human behavior in the presence of scarcity.
(SCARCITY : scarcity refers to the limitations of supply in relation to demand for a commodity)
- Positive Economics : This deals with things as they are and not what is desirable. It is the study of actual.
- Normative Economics : This deals with things as they ought to be or how the economic problem should be solved.
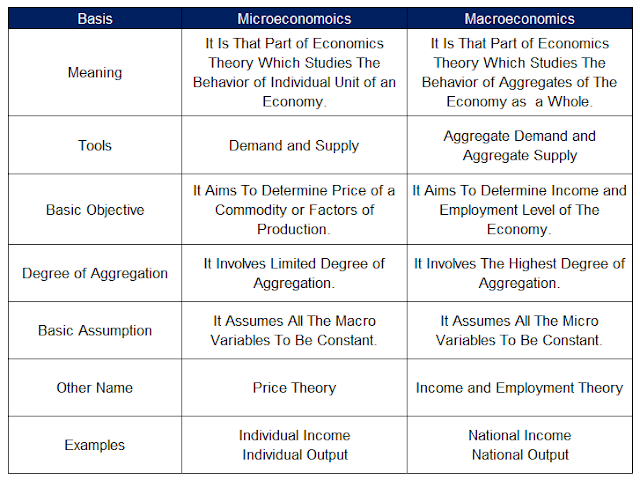
Difference Between Microeconomics and Macroeconomics
Economics Problems Of The Economy
- Positive Economics : This deals with things as they are and not what is desirable. It is the study of actual.
- Normative Economics : This deals with things as they ought to be or how the economic problem should be solved.
Economics Problems Of The Economy
- it is the problem of making choice among the scarce resources having alternative uses.
- Economic problem arises due to three reasons:
- Human wants are unlimited: humans wants are always multiplying and are endless. these unlimited demand are in excess to unlimited resources or means.
- Means are limited: the means or resources to satisfy human wants are in scarcity to fulfill unlimited human wants.
- Resources have alternative uses: Along with being scarce, the resources have alternative uses also, which makes them more scarce.
for example: A piece of land is scarce and also has alternative uses such as for cultivation, for school, for building etc.
Central Problems Of The Economy
-
It is the problem of making choice among the scarce resources having alternative uses.
(a) What to produce : It is the problem of choosing which commodity to be produced and in what quantity.
the problem of what to produce has two part:
(1) what possible commodity to produce: an economy has to decide, which consumer goods and which of the capital goods are to be produced. in the same way, economy has to make a choice between civil goods and war goods.
(2) How much to produce: After deciding the goods to be produced, economy has to decide the quantity of each commodity, that is selected. It means, it involves a decision regarding the quantity to be produced, of consumer and capital goods, civil and war goods and so on.
(b) How to produce: In this the problems of choosing the technique of production i.e to produce by using labour intensive technique or capital intensive technique.
The selection technique is made with a view to achieve the objective of raising the standard of living of people and to provide employment to everyone.
Example: In India LIT is preferred due to abundance of labour, where as countries like USA prefer CIT due to shortage of labour and abundance of capital.
(c) For whom to produce: In this the problem is of choosing the factor pricing. It means that how much of factors of production should be paid in the form of reward for their work in the form of rent, wages, interest and profits.
The problem can be categorised into two parts:
(1) personal distribution: It means how national income of an economy is distributed among different groups of people.
(2) Functional distribution: It involves deciding the share of different factor of production in the total national product of the country.
Production possibility frontier
- Meaning: It is a curve which shows all the possible combination of two goods which an economy can produce with given resources and technology.
-
Assumption of PPF:
(1) Resources are given.
(2) Resources are used fully and efficiently.
(3) Technology is given.
-
Property/ Features of PPF:(1) It is downward slopping from left to right because to gain one good we need to sacrifice other good.
(2) It is always concave to the origin due to increasing MOC.
Schedule:
- it is the problem of making choice among the scarce resources having alternative uses.
- Economic problem arises due to three reasons:
- Human wants are unlimited: humans wants are always multiplying and are endless. these unlimited demand are in excess to unlimited resources or means.
- Means are limited: the means or resources to satisfy human wants are in scarcity to fulfill unlimited human wants.
- Resources have alternative uses: Along with being scarce, the resources have alternative uses also, which makes them more scarce.
for example: A piece of land is scarce and also has alternative uses such as for cultivation, for school, for building etc.
Central Problems Of The Economy
- It is the problem of making choice among the scarce resources having alternative uses.
the problem of what to produce has two part:
(1) what possible commodity to produce: an economy has to decide, which consumer goods and which of the capital goods are to be produced. in the same way, economy has to make a choice between civil goods and war goods.
(2) How much to produce: After deciding the goods to be produced, economy has to decide the quantity of each commodity, that is selected. It means, it involves a decision regarding the quantity to be produced, of consumer and capital goods, civil and war goods and so on.
(1) what possible commodity to produce: an economy has to decide, which consumer goods and which of the capital goods are to be produced. in the same way, economy has to make a choice between civil goods and war goods.
(2) How much to produce: After deciding the goods to be produced, economy has to decide the quantity of each commodity, that is selected. It means, it involves a decision regarding the quantity to be produced, of consumer and capital goods, civil and war goods and so on.
(b) How to produce: In this the problems of choosing the technique of production i.e to produce by using labour intensive technique or capital intensive technique.
The selection technique is made with a view to achieve the objective of raising the standard of living of people and to provide employment to everyone.
Example: In India LIT is preferred due to abundance of labour, where as countries like USA prefer CIT due to shortage of labour and abundance of capital.
Example: In India LIT is preferred due to abundance of labour, where as countries like USA prefer CIT due to shortage of labour and abundance of capital.
(c) For whom to produce: In this the problem is of choosing the factor pricing. It means that how much of factors of production should be paid in the form of reward for their work in the form of rent, wages, interest and profits.
The problem can be categorised into two parts:
(1) personal distribution: It means how national income of an economy is distributed among different groups of people.
(2) Functional distribution: It involves deciding the share of different factor of production in the total national product of the country.
(1) personal distribution: It means how national income of an economy is distributed among different groups of people.
(2) Functional distribution: It involves deciding the share of different factor of production in the total national product of the country.
Production possibility frontier
- Meaning: It is a curve which shows all the possible combination of two goods which an economy can produce with given resources and technology.
- Assumption of PPF:
(1) Resources are given.
(2) Resources are used fully and efficiently.
(3) Technology is given. - Property/ Features of PPF:(1) It is downward slopping from left to right because to gain one good we need to sacrifice other good.
(2) It is always concave to the origin due to increasing MOC. Schedule:
(a) if the curve move rightward then PPF shows growth of resources.
(b) if the curve move leftward then PPF shows destruction of resources.
(c) if any point inside the the PPf curve shows under utilization of resources
opportunity cost: It refers to the cost of next best alternative.
Marginal opportunity cost: It is the additional quantity of a commodity sacrificed o produce other goods or additional units.
- Marginal Rate Of Transformation: It is the rate at which one good is sacrificed to transform it into another good.
Most important questions
Q1. Difference between microeconomics and macroeconomics?
Q2. what are economic problems of the economy?
Q3. what are the central problems of the economy?
Q4. Explain production possibility frontier?
Q5. why PPF is downward slopping?
Q6. why is PPf concave to the origin?
Q7. why MOC and MRT increasing?
(a) if the curve move rightward then PPF shows growth of resources.
(b) if the curve move leftward then PPF shows destruction of resources.
(c) if any point inside the the PPf curve shows under utilization of resources
(b) if the curve move leftward then PPF shows destruction of resources.
(c) if any point inside the the PPf curve shows under utilization of resources
opportunity cost: It refers to the cost of next best alternative.
Marginal opportunity cost: It is the additional quantity of a commodity sacrificed o produce other goods or additional units.
- Marginal Rate Of Transformation: It is the rate at which one good is sacrificed to transform it into another good.
Most important questions
Q1. Difference between microeconomics and macroeconomics?
Q2. what are economic problems of the economy?
Q3. what are the central problems of the economy?
Q4. Explain production possibility frontier?
Q5. why PPF is downward slopping?
Q6. why is PPf concave to the origin?
Q7. why MOC and MRT increasing?
Q1. Difference between microeconomics and macroeconomics?
Q2. what are economic problems of the economy?
Q3. what are the central problems of the economy?
Q4. Explain production possibility frontier?
Q5. why PPF is downward slopping?
Q6. why is PPf concave to the origin?
Q7. why MOC and MRT increasing?



Best notes for exams 👍
ReplyDeletethanku dear
DeleteThanks mam for notes
ReplyDeleteUsefull Thank You
ReplyDeleteBest notes
ReplyDeleteTremendous, fabulous,mind blowing, fantastic, super,osm, notes available in this blog
ReplyDelete